Hyperpigmentation is the medical term used to refer to dark areas on the skin that are darker than your natural skin tone. This is usually a result of excessive melanin production, which in itself has many causes.
Many of us have dealt with or have hyperpigmented areas. And although dark spots or hyperpigmentation aren’t considered dangerous, they can negatively affect our self-esteem.
Left untreated, continued UV exposure can make these dark patches permanent. As such, most people with dark spots find them unsightly and would prefer to get rid of them.
This article will cover the causes of hyperpigmentation, types of hyperpigmentation, along with prevention and treatment options.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
There are numerous reasons why areas of our skin can produce more melanin than others. Here are some common causes that can affect all skin tones to different degrees.
Sun Exposure
Oftentimes, dark spots result from overexposure to the sun or tanning beds. This excess melanin production is your skin’s way of defending itself against damage. Frequent exposure can result in sunspots, liver spots, or freckling. Areas like the face, arms, and hands are most susceptible.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal imbalances combined with sun exposure can trigger hyperpigmentation during pregnancy and menopause. This particular type of discoloration is known as melasma and is sometimes called the mask of pregnancy. They typically appear on the forehead, cheeks, and upper lip.
Medication
Certain types of medication can increase melanin production and cause hyperpigmentation. In particular, psychotropic drugs, antibiotics, tetracyclines, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, commonly known as NSAIDs.
Inflammation
Injury to the skin in the form of insect bites, cuts, acne, eczema, and even heavy scratching can lead to inflammation. Subsequently, the inflammation stimulates melanin production in the surrounding area. Dark spots that develop as a result of wound healing may become darker in the sun.
Family Genes
Although women are more susceptible to having melasma, they are not alone. Studies show that both men and women with a family history of melasma have a higher chance of developing this condition.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, and each of them has a different cause. The method of treatment will be based on the specific type as well as your complexion.
Following is a breakdown of the most common ones, which are melasma, freckles, sunspots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Melasma
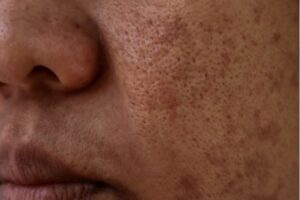
Melasma can be characterized by large patches and is the most difficult type of hyperpigmentation to treat. It often appears during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and typically shows up on the face.
There are two kinds of melasma; epidermal and dermal. Epidermal develops on the skin surface as a mild discoloration, while the other resides deeper in the skin and looks like gray-brown patches. Sun exposure plays a big part, but dermal melasma also reacts to light.
Freckles
These show up as small light or dark spots. They are hereditary and typically more apparent in lighter skin tones. They usually occur before puberty and then diminish as we get older. However, they may return after years of continued sun exposure.
People predisposed to freckling should minimize their time in the sun.
Sunspots
Also known as liver spots, show up later in life due to extended exposure to the sun. They generally appear as clumps of flat dark spots on areas like the hands, chest, and face.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH)
This type of hyperpigmentation is a result of injury or inflammation of the skin. The most common cause is inflammatory acne.
These small flat spots can appear anywhere on the body. They range in color from red, pink, brown, or black. Darker skin tones are more susceptible to developing PIH due to more intense melanin production.
Knowing the causes of hyperpigmentation and the different types is only part of the story. It is also important to understand how to prevent the dark spots from reoccurring.
Here are some measures you can take to decrease the likelihood of developing dark spots or prevent them from getting any darker.
Dark Spot Prevention
Apply sunscreen daily
Ensure that you apply sunscreen daily regardless of the season. Wear an SPF of at least 30, and reapply every two hours.
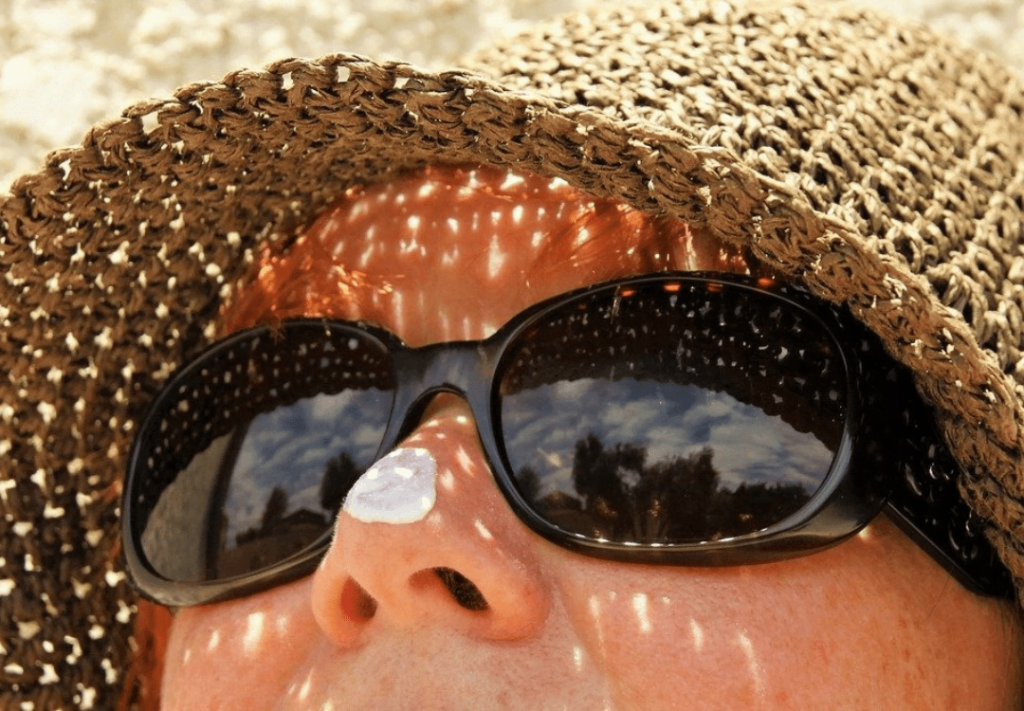
Wear hats and sunglasses

When going out in the hot sun, make sure that you cover your body adequately. Wear a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses, in addition to using sunscreen. This will give you further protection.
Treat skin conditions
Make sure to treat all skin conditions that can lead to inflammation, such as acne, appropriately. To prevent discoloration, avoid picking at pimples.
Minimize sun exposure
The sun is an excellent source of vitamin D, but too much sunlight is not recommended. Make sure that you avoid extended hours in the sun. This is usually between 10 am and 4 pm when the UV rays tend to be strongest.
Topical Solutions
Skin Exfoliators
Exfoliation works by removing dead skin cells from the top layers of the skin to fade the appearance of dark spots over time. This process also helps to boost circulation, unclog pores, and prevent acne.
Here are some of the most efficient exfoliators on the market today.
Glycolic Acid
Glycolic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that dissolves the bonds that hold the dead and discolored skin cells, making it easy to get rid of them. .
Furthermore, by using a chemical exfoliator your skin will be in a better position to absorb any treatments or serums you use afterward.
Other alpha-hydroxy acids include lactic acid, citric acid, and malic acid, which also have similar benefits.
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid, chemically known as beta hydroxy acid (BHA), is another excellent exfoliator.
It is especially effective when it comes to dark spots that result from acne because it helps clear the redness and irritation and removes all the excess oil from your pores. What’s more, it also encourages the formation of new skin cells.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that is very effective at reducing hyperpigmentation and evening out the skin tone. It . It blocks pigment production while also preventing existing pigments from getting any darker.
The best way to use this is in the form of a face serum applied directly to cleansed skin followed by a moisturizer.
Mandelic Acid
Mandelic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid made from bitter almonds. Due to its larger molecular structure, it takes longer to penetrate the skin’s surface, resulting in less irritation. It stops the growth of melanin which leads to freckles and dark spots.
This rapid exfoliator is a great option for all types of acne, including harder-to-treat cystic acne as it does not cause unwanted skin lightening.
Kojic Acid
Kojic acid is a natural skin lightener produced from mushrooms and rice. It is a popular choice for skin brightening due to its capacity to inhibit the formation of excess pigment. When properly used in safe formulations, it will not bleach your skin.
As such, it can be used by all skin tones. It works well at treating acne scars and sunspots and is a great choice for those who are sensitive to stronger brightening agents.
In addition to exfoliation, there are other ways you can treat hyperpigmentation.
Skin Lightening Creams
Over-the-counter serums and creams contain various ingredients that may speed up exfoliation and promote new skin cells.
By incorporating select ingredients, such as AHA’s, Vitamin B-3, hydroquinone, alpha arbutin, and licorice extract, lightening creams help to decrease pigmentation.
Although the most powerful at blocking melanin production, hydroquinone is slowly being discontinued from over-the-counter products, because it can be very irritating.
It should only be used for three months at a time because of the risk of ochronosis. It appears as a blue-black pigment that is virtually impossible to remove.
Skin-lightening products work efficiently on flat spots and are effective on almost all skin types. For best results, you should apply them twice a day, in the morning and at bedtime. Over time, their skin-brightening properties will start to appear.
Microneedling
This method uses fine needles to puncture the skin and create a controlled skin injury to rejuvenate the skin.
The goal of this treatment is to generate new collagen and skin cells to promote firmer, smoother, and more toned skin.
It is used primarily on the face and may treat various scars, wrinkles, and large pores. It can help to reduce hyperpigmentation by breaking up the pigment below the skin surface without damaging the epidermis.
This procedure should not be performed on skin with active acne as it will irritate the area, causing more inflammation and possibly spreading bacteria.
Retinoids
Retinoids are by-products of vitamin A. They are one of the oldest over-the-counter skincare ingredients. They have a small molecular structure, which allows them to penetrate deep into the layers of the skin below the epidermis and deal with hyperpigmentation.
Retinoids are present in OTC and prescription forms. The best is prescription since the OTC formula tends to be weaker. They can be found in serums, eye creams, and night moisturizers.
OTC retinoids have proven to be safe and effective with almost all skin tones. However, darker skin types should consult with a dermatologist for long-term use.
Bear in mind that retinoids are much more effective when it comes to dealing with wrinkles than they are with hyperpigmentation. For this reason, they may not be the best first line of treatment for hyperpigmentation.
High-Tech Options
If topical solutions aren’t addressing the problem, talk to a dermatologist about more intense ways to eliminate the discoloration.
These include chemical peels, lasers, intense pulsed light (IPL), dermabrasion, and microdermabrasion.
Chemical Peels

Chemical peels are used to treat wrinkles, scars, and discoloration on the face, neck, and hands. During this procedure, a highly concentrated chemical solution is applied to the skin and removed a few minutes later.
You may experience redness and peeling for 3 to 7 days afterward resulting in new skin growth.
The freshly peeled skin is more sensitive to the sun and should be protected with broad-spectrum sunscreen.
The best candidates for chemical peels are generally those with fair to light complexions.
Laser Skin Resurfacing
Laser skin resurfacing is performed by a dermatologist or physician. It uses light beams to remove the skin in layers to improve skin texture and appearance. There are two types of lasers; ablative and non-ablative.
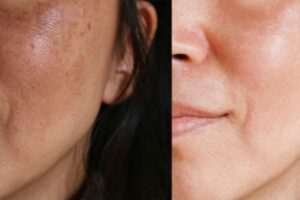
Ablative lasers consist of either carbon dioxide (CO2) or Erbium. CO2 lasers target scars and deep wrinkles, while Erbium lasers are best for superficial issues like fine lines and wrinkles.
In contrast, non-ablative lasers are used for acne-related concerns, spider veins, and rosacea. They do not remove any skin layers.
Furthermore, there are fractionated lasers, that can correct heavy sun damage on lighter skin tones. In addition, most of these lasers promote collagen growth and induce tightening.
One of the downsides of using a laser to lighten skin is that the pigment can return. This is especially true when treating melasma.
The skin is highly susceptible to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) about four weeks after treatment. As prevention, sun protection is highly recommended and laser treatments are usually done during the fall and winter seasons.
Intense Pulsed Light therapy ( IPL)
Intense pulse light therapy, also known as photofacial, is a type of , and unwanted hair. It is also used for spider veins, birthmarks, sun-damaged skin, and rosacea.
Similar to laser therapy, it uses light energy to remove dark pigment or hair follicles. However, it can target a larger area over a short period.
It is considered the first choice for lighter skin tones to tackle brown spots and freckles on the face. Results typically take three to five monthly treatments.
Dermabrasion
This procedure is used to combat age spots, injury scars, chickenpox scars, sun damage, and even acne scars.
The dermatologist uses a high-speed brush or another instrument to minimize the appearance of existing scars. The tool is fast but gentle and will resurface the entire epidermis to remove or decrease the scar depth.
Dermabrasion works best with people with fairer skin. Individuals with medium skin tones sometimes develop further hyperpigmentation after the procedure.
Microdermabrasion
This is a less intensive form of dermabrasion that is only used to treat surface scarring. The dermatologist or aesthetician utilizes a handheld device that contains an abrasive surface to remove the outer layer of skin.
More than one treatment is required and works best for people with fair skin.
Darker Skin Options
Dark skin tones have high levels of melanin and are more at risk for discoloration and PIH. When it comes to hyperpigmentation and dark spots, lighter skin tones have many more options available to them. That is not the case for those with dark complexions, as some of these treatments may do more damage than good.
 The challenge in treating the skin becomes a balance of obtaining optimal results without creating additional unwanted color in the skin or irritation. This is where an experienced dermatologist comes in.
The challenge in treating the skin becomes a balance of obtaining optimal results without creating additional unwanted color in the skin or irritation. This is where an experienced dermatologist comes in.
Some of the best brightening ingredients include vitamin C, retinoids, glycolic acid, azelaic acid, kojic acid, and . (For 20% Off Use Code: DONHIN12)
OTC lightening creams, chemical peels, microneedling, and microdermabrasion are also great picks.
For accelerated results, certain types of lasers are preferable for dark skin tones. Among them are fractionated picosecond lasers like PiQ04, PicoSure, PicoWay, Pico Genesis, and Enlighten SR.
Summary
There are various steps you can take to help minimize the appearance of existing dark spots and prevent new ones from forming. It’s all about using the right products and treatments. In particular, OTC creams, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and lasers.
An overproduction of melanin can be attributed to hormones and genetics, but the biggest offender is sun exposure.
When it comes to hyperpigmentation, melasma is tougher to treat due to its hormonal component. In some instances, it can clear up quickly, while taking longer in others. For some people, treatments must be repeated indefinitely.
With excessive sun exposure, melasma can return after fading. That is why recurrence is normally more visible during the summer months. Daily application of a full-spectrum sunscreen is vital in preventing this.
As described, skin discoloration is not all the same, and the specific type will influence the method of treatment. Treatments are based on your complexion, and some can make discoloration worse.
What may work for one person may not be good for another. Each person’s response to treatment is different, so they must be considered on an individual basis.
For personalized treatment consult a qualified dermatologist to help determine the exact cause of the hyperpigmentation. Through their expertise, they can formulate a regimen that is designed to produce the best possible results for your skin type.